Starting from the 10th century the Arab-African Swahili culture developed in East Africa. The Arabs established from the 11th century commercial settlements at the coast. A prosperous trade with ivory and slaves began. In the 16th century the Portuguese occupied the coast and settled.
The British proclaimed 1895 in Kenya the protectorate East Africa, 1920 became Kenya crown colony, 1922 became it part of British East Africa.
Native tribes initiated 1952 the “Mau -Mau“- rebellion which was lasting until 1955/56. 1963 became Kenya within the Commonwealth its independency, 1964 became it republic.
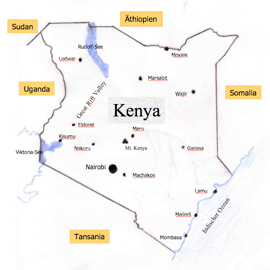
Today is Kenya a Semi- Presidential Republic with an area of 582,646 square km acreage and 36.9 million inhabitants (2007). It lies in east Africa on the Indian Ocean. The capital city is Nairobi, the official languages are Swahili and English.
In Kenya living more than 50 ethnic groups and they speak in more than 60 different languages. Most inhabitants are members of the Bantu people, Kikuyu, Luhya, Kamba und Kisii. The Kikuyu are with 22% the largest folk in Kenya. Some nilotic and hamito-nilotic ethnic groups like Kalenjin, Luo, Massai Samburu and Iteso, as well as smaller ethic groups like the El-Molo, Niemps and Rendille domicile in Kenya.
Kenya is a country crossed from north to south by rifts and graben in the western part (East African Continental Rift), partly of volcanic landscape with elevated veldt plains. The highest elevation, the Batian with 5,199 meter, lies in the Mount Kenya area. Precipitations are higher in the western part and in the coast only. Neighbour countries are Tanzania, Uganda, Sudan, Ethiopia, Somalia.
Agrarien cultivation: Mais, manioc, sugar cane, for exporting, partly in plantations: Coffee, Tea, Sisal; animal husbandry.
The British proclaimed 1895 in Kenya the protectorate East Africa, 1920 became Kenya crown colony, 1922 became it part of British East Africa.
Native tribes initiated 1952 the “Mau -Mau“- rebellion which was lasting until 1955/56. 1963 became Kenya within the Commonwealth its independency, 1964 became it republic.
Today is Kenya a Semi- Presidential Republic with an area of 582,646 square km acreage and 36.9 million inhabitants (2007). It lies in east Africa on the Indian Ocean. The capital city is Nairobi, the official languages are Swahili and English.
In Kenya living more than 50 ethnic groups and they speak in more than 60 different languages. Most inhabitants are members of the Bantu people, Kikuyu, Luhya, Kamba und Kisii. The Kikuyu are with 22% the largest folk in Kenya. Some nilotic and hamito-nilotic ethnic groups like Kalenjin, Luo, Massai Samburu and Iteso, as well as smaller ethic groups like the El-Molo, Niemps and Rendille domicile in Kenya.
Kenya is a country crossed from north to south by rifts and graben in the western part (East African Continental Rift), partly of volcanic landscape with elevated veldt plains. The highest elevation, the Batian with 5,199 meter, lies in the Mount Kenya area. Precipitations are higher in the western part and in the coast only. Neighbour countries are Tanzania, Uganda, Sudan, Ethiopia, Somalia.
Agrarien cultivation: Mais, manioc, sugar cane, for exporting, partly in plantations: Coffee, Tea, Sisal; animal husbandry.